What We Do
Virtual Reality and Artificial Intelligence Research and Software Development
VRAIL – Virtual Reality & Artificial Intelligence Lab facilitates scientific and interdisciplinary VR/AR/AI research in neuroscience and neuroscience-related studies such as psychology, radiology, forensics, anthropology, and several other medical fields where computer-driven 3d visualization, scientific-testing, simulation/modeling, and experimentation are required.
Services include:
- VR/AR/AI Software Development (Unreal/Unity)
- Neural Resonance Field Tools
- Custom AI (Bots and Analysis)
- Grant Writing/Development
- Custom AI Image Tools (Stable Diffusion)
- OpenAI API Integrations
- HIPPA Compliant AI Tools and App Development
- Local AI GPU Processing (CUDA)
- Scientific VR/AR Environmental Design/Production
- Large Language Model (LLM) Analysis/Tools (Llama 2)
- VR Simulation Modeling
- Mobile/PC Software Development (tablet/mobile)
- Environment Scanning/Modeling (terrestrial/drone)
- VR/AR Experimental/UX Design
- VR/AR Experimentation
- Subject Testing
F
Located in the Brain Science Center, the laboratory broadly operates as a virtual, augmented reality, and artificial experimentation and collaboration space, software development laboratory, subject-testing, and experimentation facility for research incorporating virtual and augmented reality. The lab is equipped with state-of-the-art computer hardware (high-end RTX/CUDA GPU systems) and a multitude of virtual and augmented reality headsets are available for use.
Some of our Projects
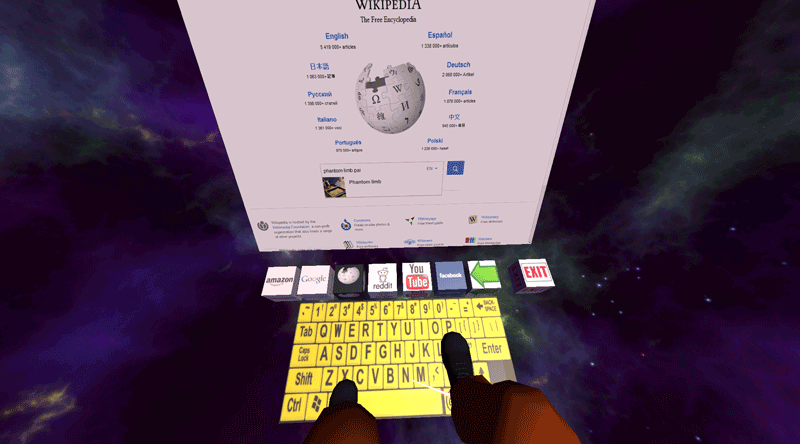
Phantom Limb Pain
Essentially mirror box therapy done with Virtual Reality. Custom built games and a web browser provide a greater sense of agency over phantom limbs and a more compelling illusion while engaging the patient.

Hemispatial Neglect
We are using an eye-tracking VR headset with the Leap Motion to examine how subjects with Hemispatial Neglect explore their environments when presented with various arrangements of objects in peripersonal and extrapersonal space.
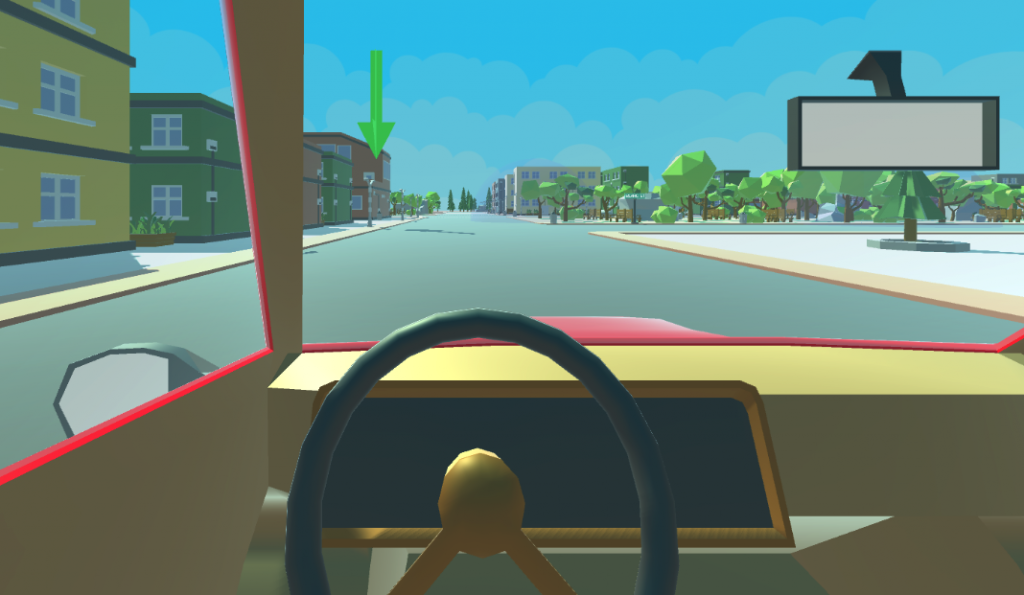

Navigation Brain Mapping
Subjects play taxi driver in a VR city, then play again on a regular screen while having their brain scanned.

Broca's Aphasia
An intervention for Broca’s Aphasia that sets subjects in front of a mirror in VR. As they speak, they will see an avatar that looks exactly like them correctly mouth their words.

Arch
Explores the psychological effects of varying certain architectural features by letting subjects compare and explore rooms in VR.
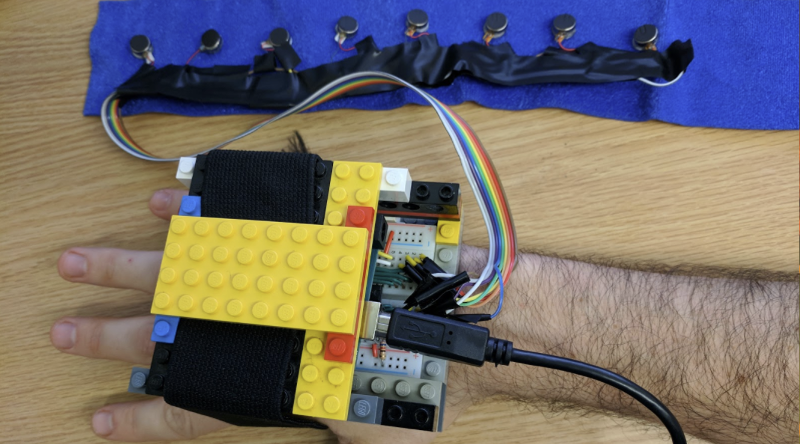
Vibrotactile Compass
Explores the impact of a vibrotactile compass on navigation in a setting without any visual cues. Subjects strap on a compass that indicates north by activating buzzers, follow a short path that disappears, and then indicate their origin.
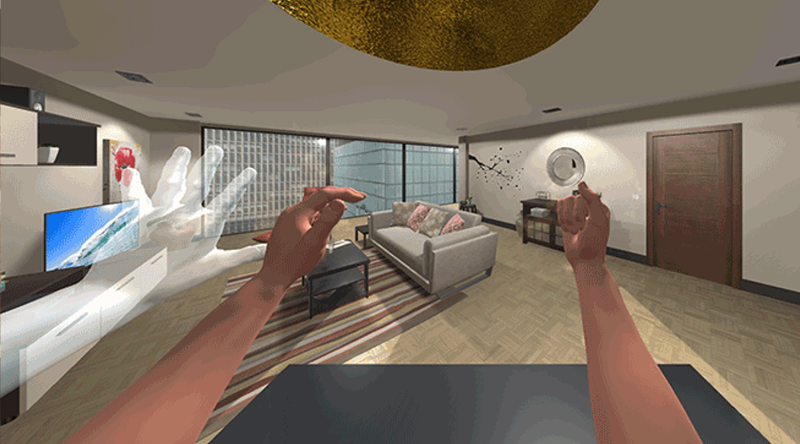

Hemiparesis
An intervention for people with Hemiparesis in which symmetrical movements are preformed with hands manipulated with novel control schemes enabled by Leap Motion.
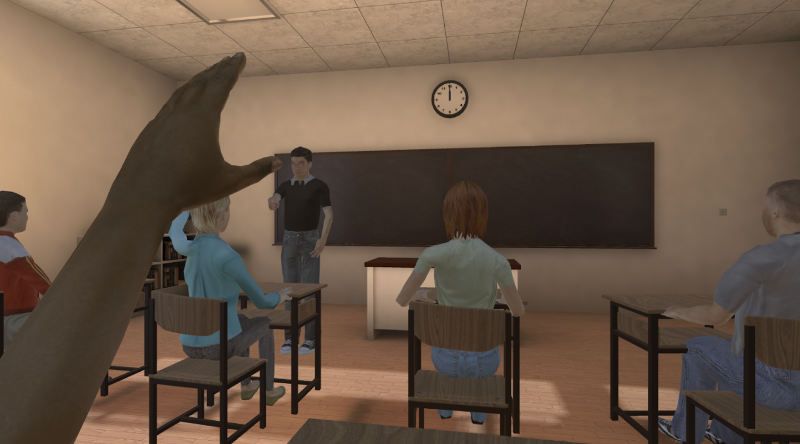

Racial Empathy
Explore racial empathy by embodying different races in VR and experiencing interactions affected by prejudice.
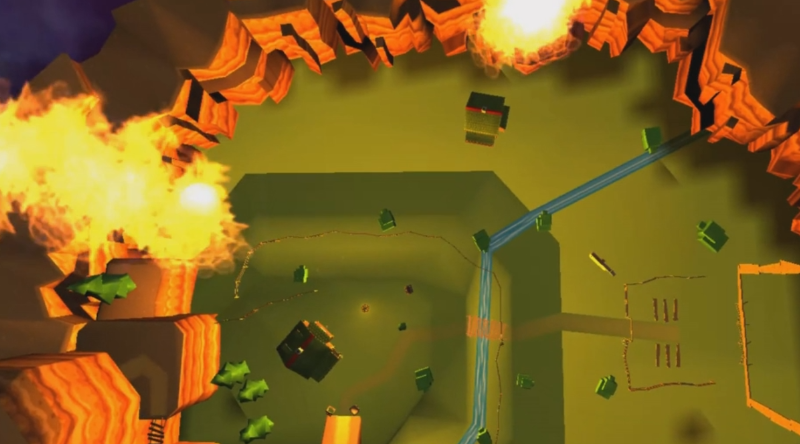

Retinitis Pigmentosa
An engaging intervention for Retinitis Pigmentosa in which a subject’s peripheral vision is precisely stimulated by meteors that hover in place before moving towards targets in a game akin to Missile Command.
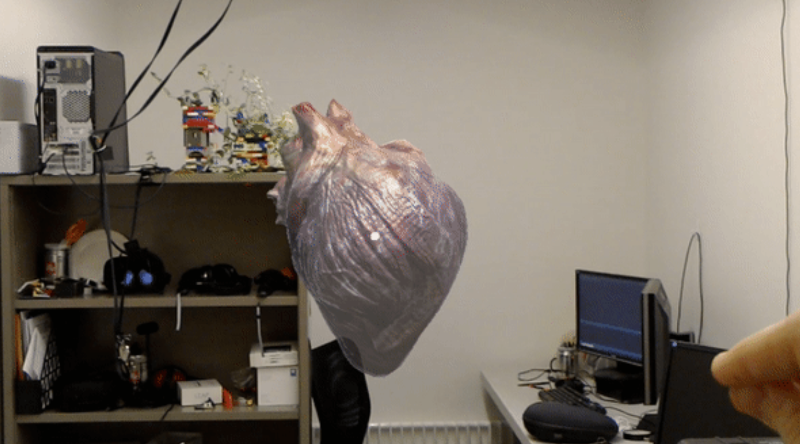

Echocardiogram Visualizer
An application for the Microsoft Hololens that renders 3D echocardiograms. We’re also exploring CT scan overlay for surgeons.

Affordance Memory
Explores effects of subtle geometric changes on memory with a series of trials in which subject must collect and then replace various objects.
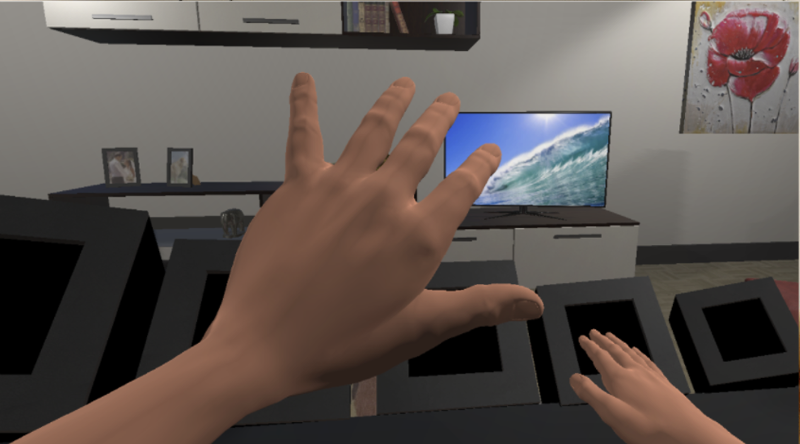

Hand Magnification
Explores sensory effects of magnifying or shrinking one of the subject’s hands.
Who We Are

Jeffrey R. Vadala PhD
Director
jeffrey.vadala@pennmedicine.upenn.edu
Dr. Jeffrey R. Vadala is the lab’s director and lead Unreal Engine and Unity programmer. His research broadly explores human perception of landscapes and architectural spaces and how they shape both cognitive and cultural processes in contemporary and archaeological contexts. Utilizing both virtual reality and augmented reality tools, his doctoral research historically traced the historical processes associated with the development of human perception at ancient Maya sites in the Yucatan and Belize. As the director of the Penn Neurology VR Laboratory, he currently works as a collaborator and software developer with the goal of bringing virtual and augmented reality approaches and experimental methods to neuroscience, psychology, anthropology, and medical researchers. He obtained his Ph.D. in anthropological archaeology from the University of Florida in 2016.

Vicente Estrada Gonzalez PhD
Postdoctoral Researcher
vicente.estradagonzalez@pennmedicine.upenn.edu
Estrada Gonzalez studied how viewers perceive art using eye-tracking technology during a PhD program at the University of New South Wales. The research explored how different viewing contexts, including digital displays, museums, and VR, impact perception. At VRAIL Estrada Gonzales is developing new eye-tracking biofeedback recording techniques for use in VR and AI applications. At the nearby Penn Center for Neuroaesthetics, Estrada Gonzalez now examines how nature-inspired virtual reality designs influence cognition and emotions. Previously, at the Universidad Nacional Autonoma de Mexico, Estrada Gonzalez conducted research on the role of the endocannabinoid system in drug addiction. Estrada Gonzalez also founded a curatorial project, Mexico Sensible, in 2013.
Reach Out
jeffrey.vadala@pennmedicine.upenn.edu